[ad_1]
Juvenile delinquency in India has
emerged as a significant socio-legal challenge, with a complex interplay of
factors contributing to criminal behavior among children below 18 years of age.
The problem requires urgent attention as recent statistics indicate concerning
trends in youth crime patterns across the country.
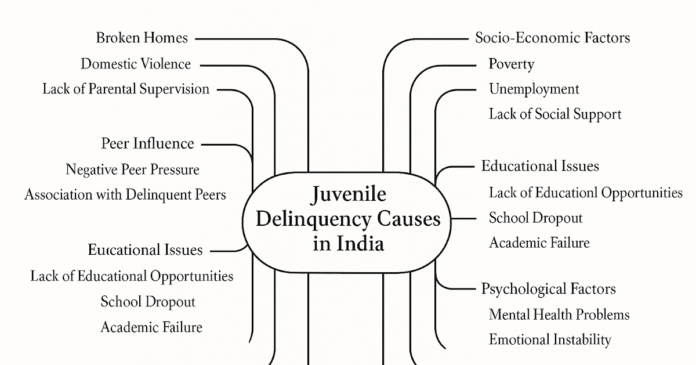
Major Causes of Juvenile Delinquency in
India
1. Socio-Economic Factors
Poverty
and Economic Hardship
Poverty remains the most pervasive
driver of juvenile delinquency in India. Economic deprivation creates a cycle
where children from impoverished backgrounds engage in criminal activities to
support themselves or their families. The lack of basic necessities such as
food, shelter, clothing, and education forces juveniles to earn money through
illegal means.
Children living in slums face numerous
challenges including inadequate access to education, healthcare, and
recreational activities. The frustration and hopelessness resulting from
economic hardship often push juveniles toward illegal activities as a means of
survival or financial gain.
Unemployment
and Lack of Opportunities
Unemployment among youth exacerbates
the problem significantly. When legitimate job opportunities are scarce, young
people become idle and susceptible to criminal activities. Studies indicate
that 77% of youth criminals are
unmarried and have fewer responsibilities, while 40% come from lower economic classes with incomes below Rs. 1,500
per month
Research shows that poverty and
unemployment lead people to commit crimes, particularly money-related offenses.
The economic instability creates an environment where juveniles view crime as
their only viable survival option.
2. Family-Related Factors
Broken
Homes and Family Dysfunction
Family disintegration is one of the
leading causes of juvenile delinquency. Broken homes result from various
circumstances including parental death, serious health problems, parents living
far away for work, or divorce. Children from such environments lose parental
love and control, becoming vulnerable to anti-social influences.
Studies reveal that family dysfunction,
including parental neglect, domestic violence, substance abuse, and inadequate
supervision, significantly contributes to delinquent behavior. 84% of married girls aged 15-19 years have
the highest school dropout rate, followed by unmarried girls (46%) and boys
(38%).
Parental
Factors
Inadequate parental guidance and lack
of constant monitoring are critical factors. When parents fail to provide
proper supervision, children are more likely to engage in criminal activities.
Parents in poor homes often work long hours, leaving children uncared for and
vulnerable to gangster influence.
The absence of proper parental
interaction and discriminatory practices by parents increase the likelihood of
school dropout and subsequent delinquency. Children who feel neglected or
unloved by their parents may turn to crime due to aggression and negative
feelings
3. Educational Challenges
High
Dropout Rates
Educational challenges play a
significant role in juvenile delinquency. The dropout rate increases with the stage of schooling, and more girls
drop out than boys at higher levels. Primary school dropout averages 9% nationally, middle school 18%, and high school 16%.
Key factors contributing to educational
dropout include:
·
Financial constraints preventing families from affording
education costs
·
Child labor as children work to support family income
·
Lack of interest in studies (43% among younger boys)
·
Family reasons (23%) and paid work requirements (21%)
Children engaged in paid work are
significantly more likely to drop out: younger boys are 6.67 times more likely and girls 2.56 times more likely to leave school.
4. Social and Peer Influences
Bad
Company and Peer Pressure
Peer groups, neighbors, and companions
significantly impact child behavior. Association with delinquent peer groups
often leads to changes in attitude and increased likelihood of criminal
behavior. Studies identify peer pressure and negative peer influence as
significant factors precipitating antisocial conduct.
The influence of gang subculture and
lack of positive social support systems contribute to juvenile involvement in
criminal activities. Children from areas with high crime rates are more
susceptible to adopting illegal modes of earning money.
Social
Media and Technology Influence
The advent of technology and social
media has introduced new forms of juvenile crime. Cybercrime, including hacking, online fraud, and cyberbullying, is
rising among young people. Social media addiction correlates with increased
juvenile crime among teenagers in India.
Studies reveal that exposure to violent
content, cyberbullying, online harassment, and inappropriate material on social
media platforms contributes to behavioral deviance. The anonymity of the
internet often emboldens juveniles to engage in criminal activities.
5. Substance Abuse
Drug and
Alcohol Dependency
Substance abuse is strongly correlated
with juvenile delinquency. Research indicates that 86.44% of juveniles under enquiry had a history of substance use.
The primary substances include:
·
Tobacco and cannabis (most common)
·
Alcohol (prevalent among violent crime offenders)
·
Opioids/heroin (higher in mugging and snatching
crimes)
·
Solvents/inhalants (16.2% among rape convicts)
India has witnessed a 70% rise in narcotic consumption over
eight years, with 13% of drug abuse
victims below age 20. Children face increased risk due to poor mental and
physical health resulting from violence, exploitation, and sexual abuse.
6. Urbanization and Migration
Displacement
and Urban Challenges
Rapid urbanization and migration
contribute significantly to juvenile crime. Families migrating to cities often
end up in slums and impoverished neighborhoods lacking adequate infrastructure
and support systems.
Young people from remote villages
migrating for better opportunities often become susceptible to illegal earning
methods due to displacement and instability. 62% of youth criminals are from urban areas compared to 38% from
rural areas.
7. Biological and Psychological Factors
Mental
Health Issues
Mental instability is observed among
many juvenile delinquents. Children suffering from mental deficiencies or
illnesses cannot distinguish between right and wrong, making them vulnerable to
exploitation by criminals.
Emotional
problems such as
jealousy, inferiority complex, and feeling that society is against them
contribute to delinquent behavior. When children feel denied their basic rights
or improperly treated, they may turn to criminal activities.
8. Legal and Systemic Issues
Implementation
Gaps
Despite progressive legislation like
the Juvenile Justice (Care and Protection of Children) Act 2015, implementation
remains inconsistent across states. This leads to disparities in juvenile
treatment and rehabilitation.
Recidivism
Concerns
The most alarming trend is the increase in recidivism from 1,187 in 2021
to 1,539 in 2022. This sharp rise raises serious concerns about the
effectiveness of current rehabilitation and intervention programs.
Conclusion
Juvenile delinquency in India is a
multifaceted problem requiring comprehensive intervention strategies. The
primary causes include poverty, family dysfunction, educational challenges,
peer influence, substance abuse, urbanization effects, mental health issues,
and systemic implementation gaps. Understanding these interconnected factors is
crucial for developing effective prevention and rehabilitation programs that
address root causes rather than merely treating symptoms.
The rising trend in violent crimes and
recidivism among juveniles necessitates urgent policy reforms focusing on
strengthening family support systems, improving educational access, addressing
socio-economic inequalities, and enhancing rehabilitation programs. A holistic
approach involving community participation, educational reforms, and targeted
interventions is essential to combat this growing social challenge effectively.
Juvenile Delinquency in India: Easy Study Guide
-
Definition and Current Scenario
Juvenile delinquency in India refers to crimes committed by individuals below 18 years. It accounts for about 0.9-1% of total crimes, with violent crimes rising from 32.5% in 2016 to 50% in 2022, showing a concerning upward trend.
-
Socio-Economic Factors
Poverty and unemployment are primary drivers, with many juveniles from poor families engaging in crime for survival. About 40% of youth criminals earn less than Rs. 1,500 per month, and slum living conditions exacerbate vulnerabilities.
-
Family-Related Causes
Broken homes, parental neglect, domestic violence, and lack of supervision contribute significantly. Children from dysfunctional families often lack guidance and emotional support, increasing their risk of delinquency.
-
Educational Challenges
High dropout rates, especially among girls, contribute to juvenile crime. Financial hardship, child labor, and lack of interest lead many juveniles to leave school early and turn to criminal activities.
-
Peer Pressure and Social Influence
Negative peer groups, gang affiliation, and social media exposure play critical roles. Juveniles influenced by bad company and online violence are more likely to engage in delinquent behavior.
-
Substance Abuse
A large proportion (around 86%) of juvenile offenders have a history of substance use, including tobacco, cannabis, alcohol, and opioids, which impairs judgment and amplifies criminal tendencies.
-
Urbanization and Migration
Migration from rural areas to cities for better opportunities often results in juvenile displacement, poverty, and involvement in crime, with 62% of juvenile offenders residing in urban areas.
-
Biological and Psychological Factors
Mental health issues, emotional trauma, and psychological disorders reduce juveniles’ ability to discern right from wrong, making them prone to illegal activities.
-
Legal and Systemic Issues
Though laws like the Juvenile Justice Act exist, implementation gaps and inconsistent rehabilitation efforts contribute to rising recidivism, with 1,539 repeat juvenile offenders reported in 2022.
-
Interconnectedness of Causes
Juvenile delinquency arises from the complex interaction of economic hardship, family dysfunction, educational failure, social environment, substance abuse, psychological issues, and systemic challenges, requiring holistic prevention and intervention strategies.
Quick Memory Formula:
“SPUFS-BUL”
This acronym will help you remember all
8 major causes:
·
S – Socio-economic factors
·
P – Peer pressure & social influence
·
U – Urbanization & migration
·
F – Family factors
·
S – Substance abuse
·
B – Biological/psychological factors
·
U – Unemployment & education
·
L – Legal/systemic issues
Simple Story Method for Memory
“Poor
Raju’s Journey to Crime”
Poor Raju (poverty) lived in a broken
family (family issues). He dropped out of school (education) and moved to the
city (urbanization). There he met bad friends (peer pressure), started drinking
(substance abuse), became depressed (psychological issues), and when caught,
the system failed him (legal issues).
This single story covers all 8 major
causes!
Memory Palace Technique
Imagine
walking through a house:
1. Front
door (Entry) = Poverty (can’t afford to enter properly)
2. Living
room = Family issues (family gathering place)
3. Study
room = Education problems (obvious connection)
4. Kitchen = Substance
abuse (where substances are)
5. Bedroom = Peer
pressure (private space where friends influence)
6. Bathroom = Psychological
issues (where you look in mirror)
7. Balcony = Urbanization
(view of the city)
8. Back door = Legal
system (exit/escape route)
[ad_2]
Source link